MEMORY SLOTS & EXTERNAL CACHE :-
Memory, or Random Access Memory(RAM), Slots are the next most prolific slots on a motherboard, & they contain the modules that hold memory chips that make up primary memory. In this session we will become familiar with the appearance & specifications of the slots on the motherboard.
Today's most of the memory chips arranged on a small circuit board. These circuit boards are called DIMMs (Dual inline memory modules). Today's DIMMs differ in the number of conductors, or pins that the particular physical specification uses.
Some Common examples
* 30 Pin
* 72 Pin
* 144 Pin
* 168 Pin
* 184 Pin
* 240 pin configuration
Laptop memory comes in smaller form factors known as SODIMMs (Small outline DIMMs) & MicroDIMMs.
The single inline memory module (SIMM) is an older form factor.
SIMM Slots
Memory slots are easy to identify on a motherboard. DIMMs slots are usually black & placed very close together.
DIMM slot
DIMM slots with pair - by - pair color coding can be observed these days. Generally the pairs of slots must be filled together for best performance or to work at all in some cases.
The number of memory slots varies from motherboard to motherboard, but the structure of the different slots is similar. Metal pins in the bottom make contact with the metallic pins on each memory module. small metal or plastic tabs on each side of the slot keep the memory module securely in its slot.
SODIMMs slot
MicroDIMMs slot
External cache:-
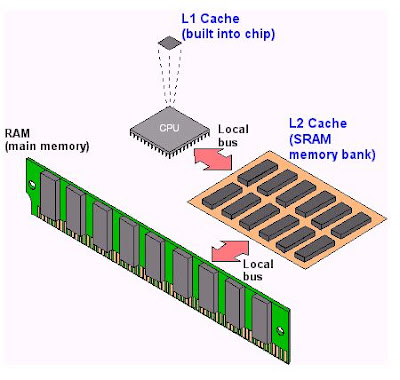
Cache is a very fast form of memory forged from static RAM. Cache improves system performance by predicting what the CPU will ask for next & prefetching this information before being asked. This paradigm allows the cache to be smaller in size than the RAM itself.
Only the most recently used data & code or that which is expected to be used next is stored in cache. Cache on the motherboard is known as external to the processor, also referred to as "Level-2" (L2) cache. "Level-1"(L1) cache, by comparison is internal cache because it is built into the processor's silicon wafer.
It is now common for chip makers to use extra space in the processor's packaging to bring the L2 cache from the motherboard closer to the CPU. When the L2 cache is present in the processor's packaging, the cache on the motherboard is referred to as "Level-3"(L3) cache.
Unfortunately, due to the de facto naming of cache levels. the term L2 cache alone is not a definitive description of where the cache is located. The terms L1 cache & L3 cache do not vary in their meaning, however. The typical increasing order of capacity & distance from the processor die is L1 cache, L2 cache, L3 cache, RAM.





Comments
Post a Comment