CPU / Processors Slots & Sockets:-
The "Brain"of any computer is the CPU "Central Processing Unit". There is no computer without CPU. There are different type of processors are used in computers from the beginning,(we will discuss about them later in other post)different type of processor means different type of slots/sockets which is present on the motherboard.
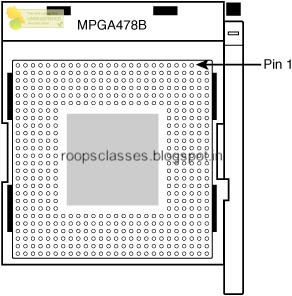
Sockets & slots on the motherboard are almost as plentiful & as processors. Sockets are basically flat & several rows of holes or pins arranged in a square. Sockets are of two types PGA & LGA . PGA sockets has holes to receive the pins on the processor, Where as LGA has spring-loaded pins in the socket & a grid of lands on the processor. The LGA is a newer technology that places the delicate pins on the cheaper motherboard, not the more expensive processor, opposite to the way the aging PGA does. The device with the pins has to be replaced if the pins become too damaged to function.
Modern Processor sockets have some sort of mechanism in place that reduces the need to apply the considerable force to the CPU that was necessary in the early days of personal computing to install a processor. Given the extra surface area on today's processors, excessive pressure applied in the wrong manner could damage the CPU packaging, its pins, or the motherboard itself. For Processors based on the PGA concept, "Zero Insertion Force"(ZIF) sockets are exceedingly popular. ZIF sockets use a plastic or metal lever on one edge to lock or release the mechanism that secures the processor pins in the socket. The processor rides on the mobile top portion of the socket.
For processors based on the LGA concept, a socket with a different locking mechanism is used. Because there are no receptacles in either the motherboard or the processor, there is no opportunity for a locking mechanism that holds the component with the pins in place.
PGA socket
LGA socket
LGA compatible sockets, as they're called despite the misnomer, have a lid of sorts that closes over the processor & is locked in place by an L -Shaped arm that borders two of the socket's edges. The non locking leg of the arm has a bend in the middle that latches the lid closed when the other leg of the arm is secured.
The processor slot is another method of connecting a processor to a motherboard, but one into which a processor (such as the AMD Athlon or Intel Pentium II or Pentium III) on a special expansion card is inserted.
Modern Processor sockets have some sort of mechanism in place that reduces the need to apply the considerable force to the CPU that was necessary in the early days of personal computing to install a processor. Given the extra surface area on today's processors, excessive pressure applied in the wrong manner could damage the CPU packaging, its pins, or the motherboard itself. For Processors based on the PGA concept, "Zero Insertion Force"(ZIF) sockets are exceedingly popular. ZIF sockets use a plastic or metal lever on one edge to lock or release the mechanism that secures the processor pins in the socket. The processor rides on the mobile top portion of the socket.
For processors based on the LGA concept, a socket with a different locking mechanism is used. Because there are no receptacles in either the motherboard or the processor, there is no opportunity for a locking mechanism that holds the component with the pins in place.
PGA socket
LGA socket
LGA compatible sockets, as they're called despite the misnomer, have a lid of sorts that closes over the processor & is locked in place by an L -Shaped arm that borders two of the socket's edges. The non locking leg of the arm has a bend in the middle that latches the lid closed when the other leg of the arm is secured.
The processor slot is another method of connecting a processor to a motherboard, but one into which a processor (such as the AMD Athlon or Intel Pentium II or Pentium III) on a special expansion card is inserted.
Different type of Slots & sockets:-
SLOT 1
SLOT 2
SOCKET 1,2,3,6
SOCKET 4,5,7,8
SOCKET 370
SOCKET 423











Comments
Post a Comment